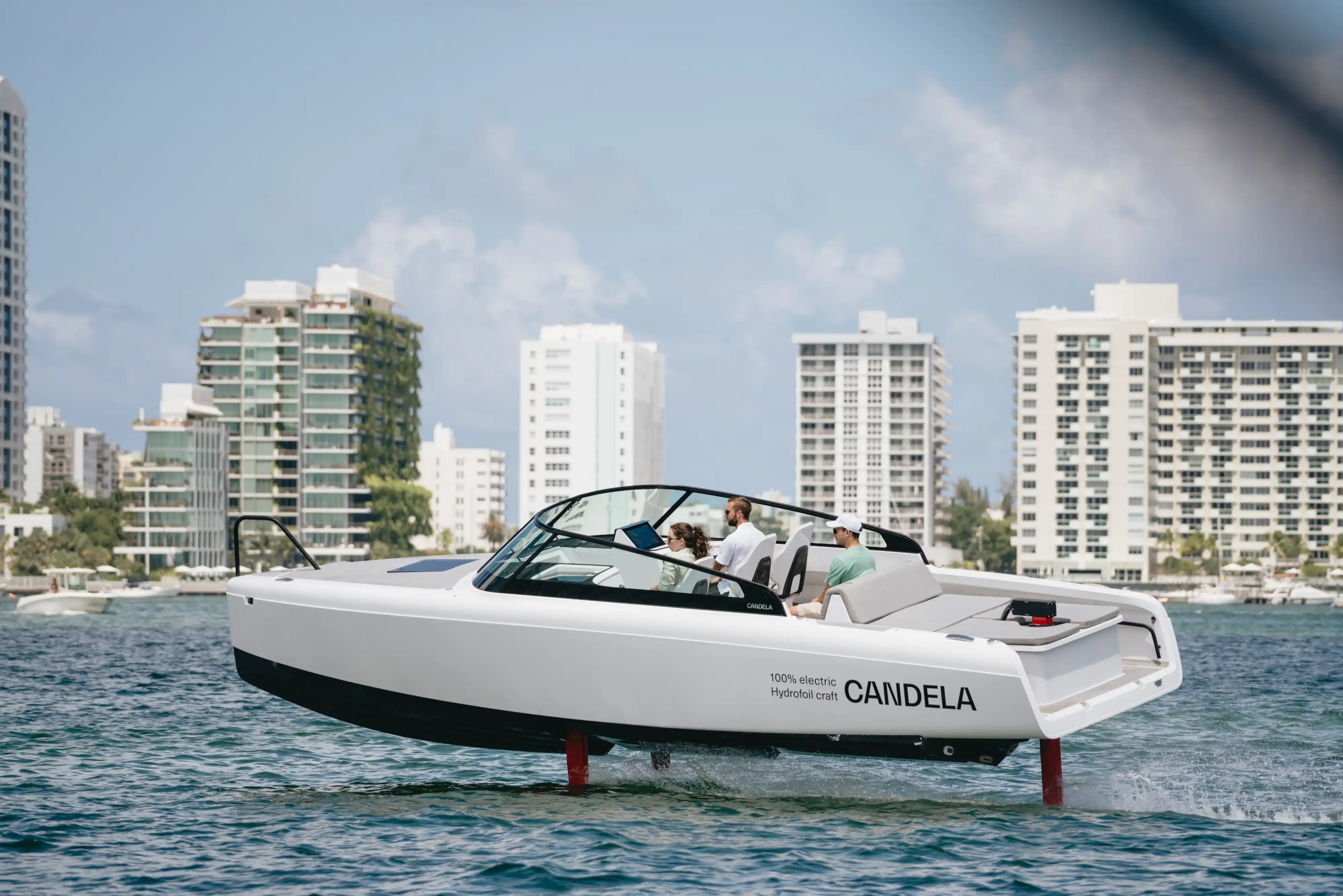
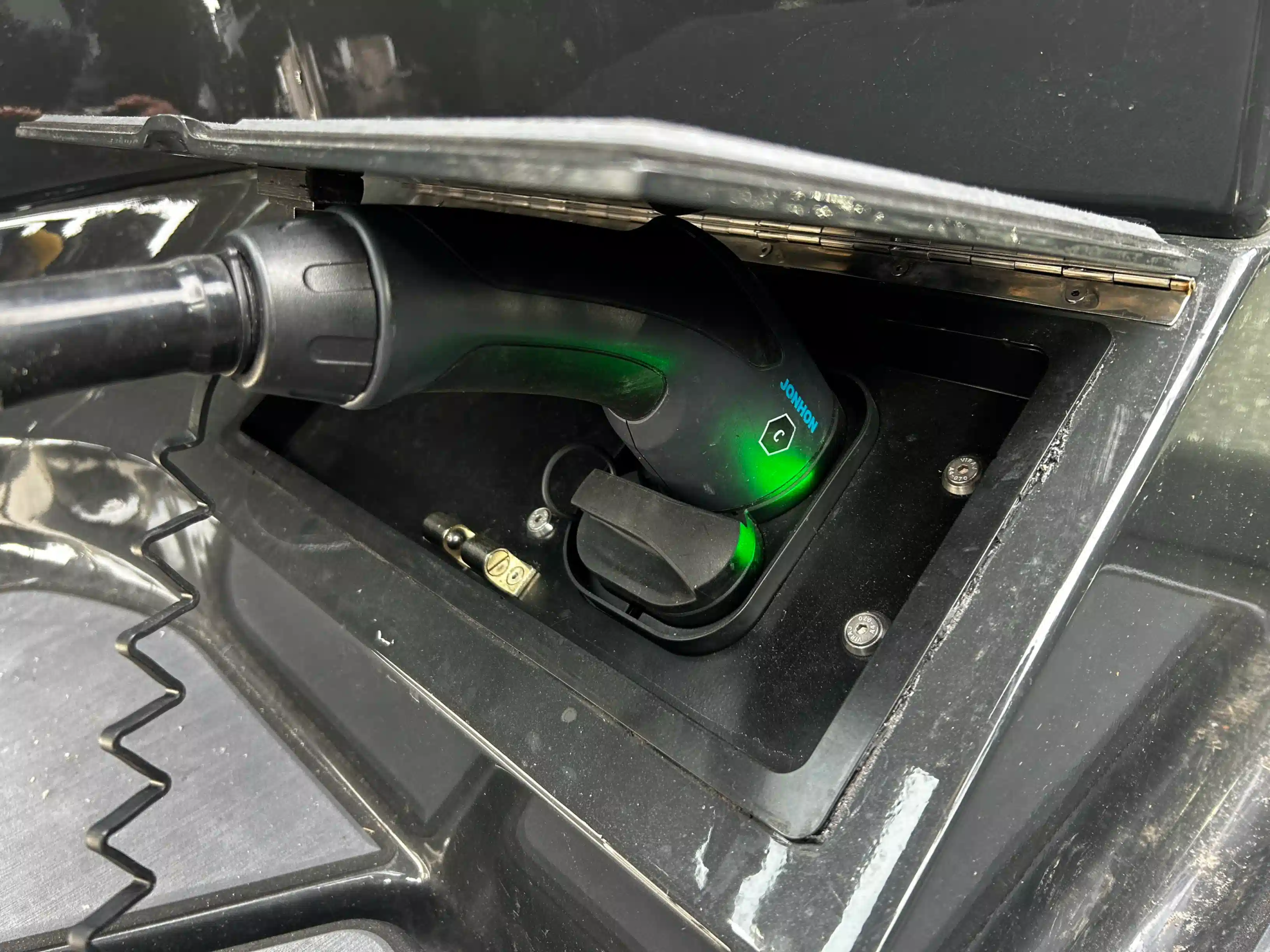
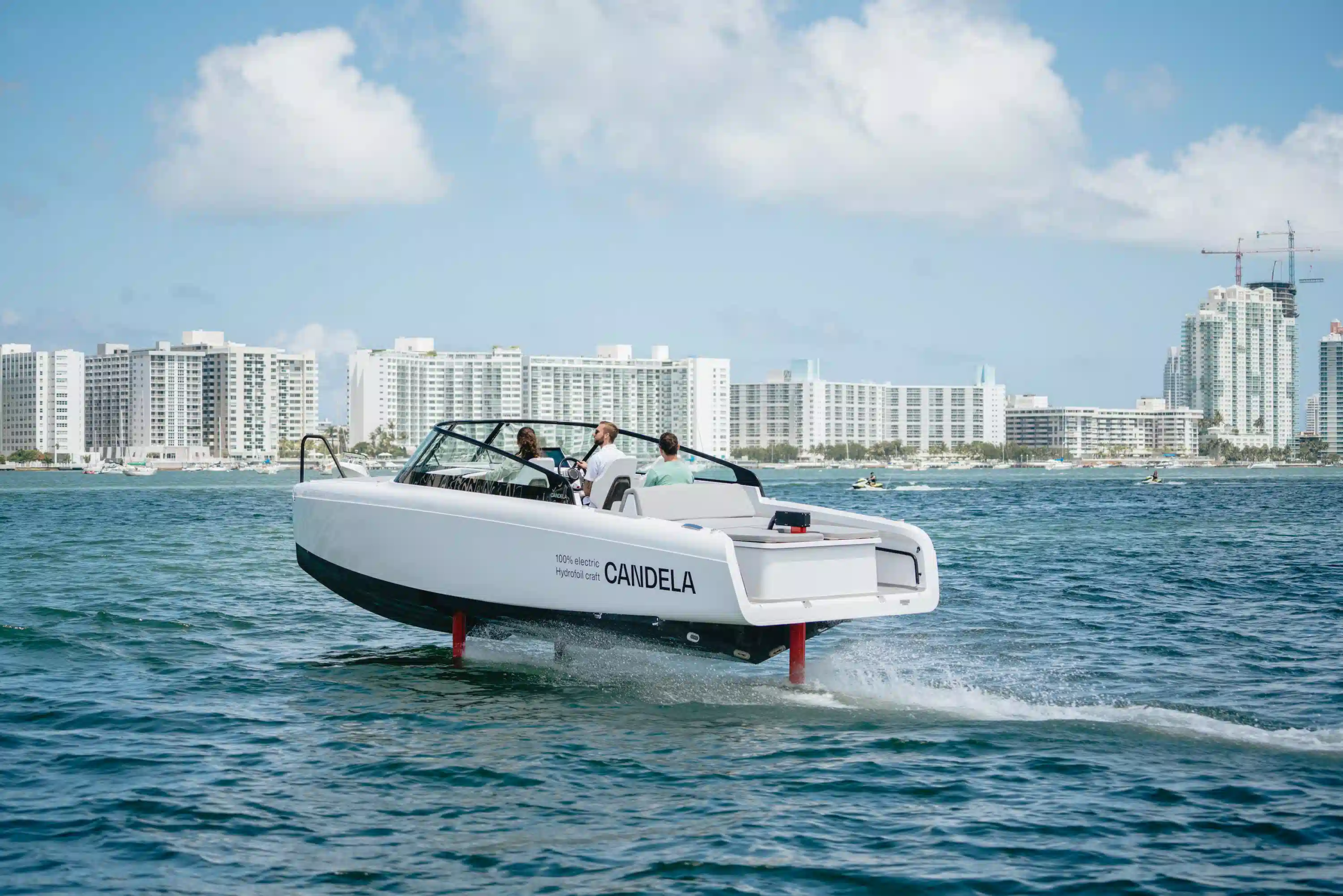
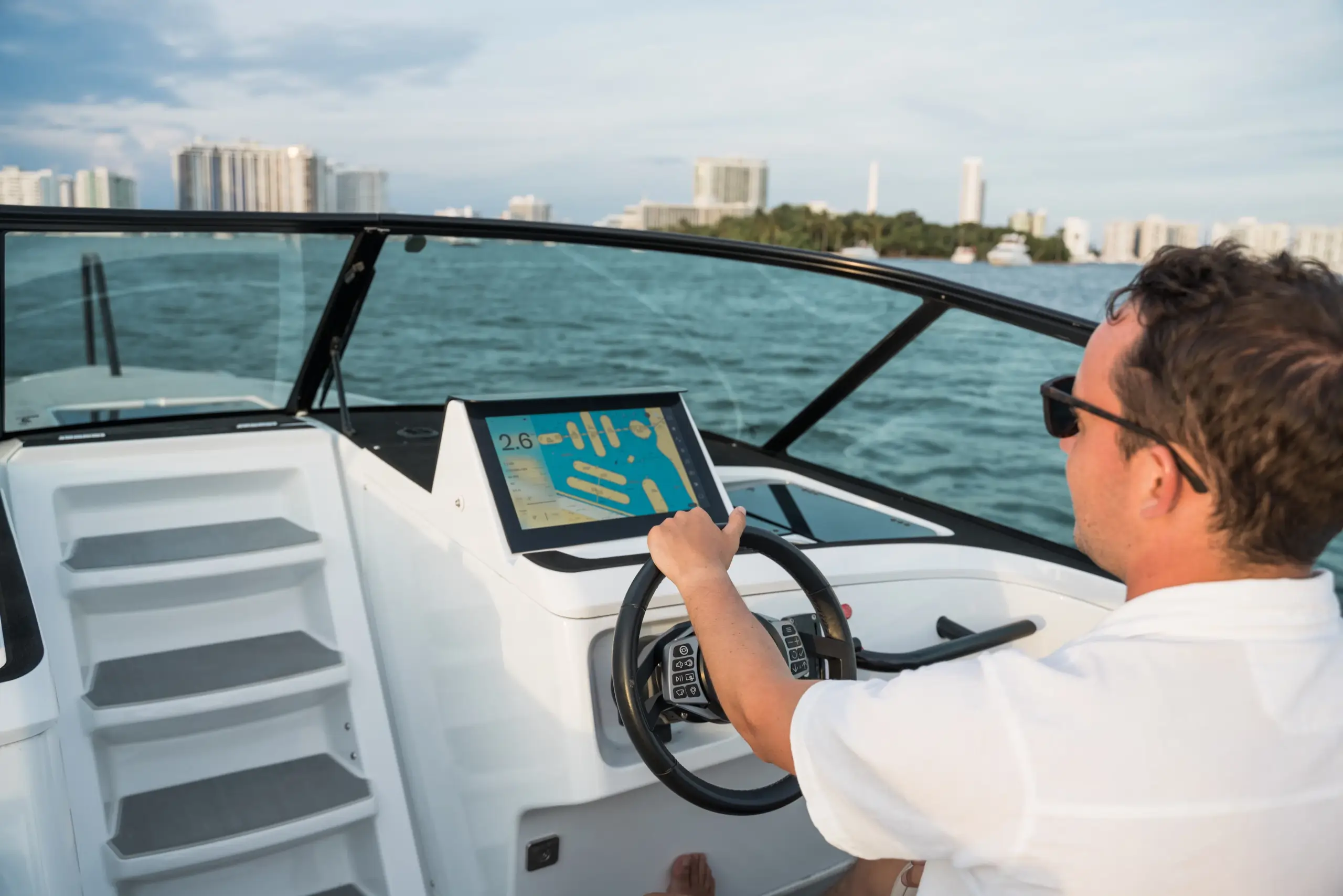
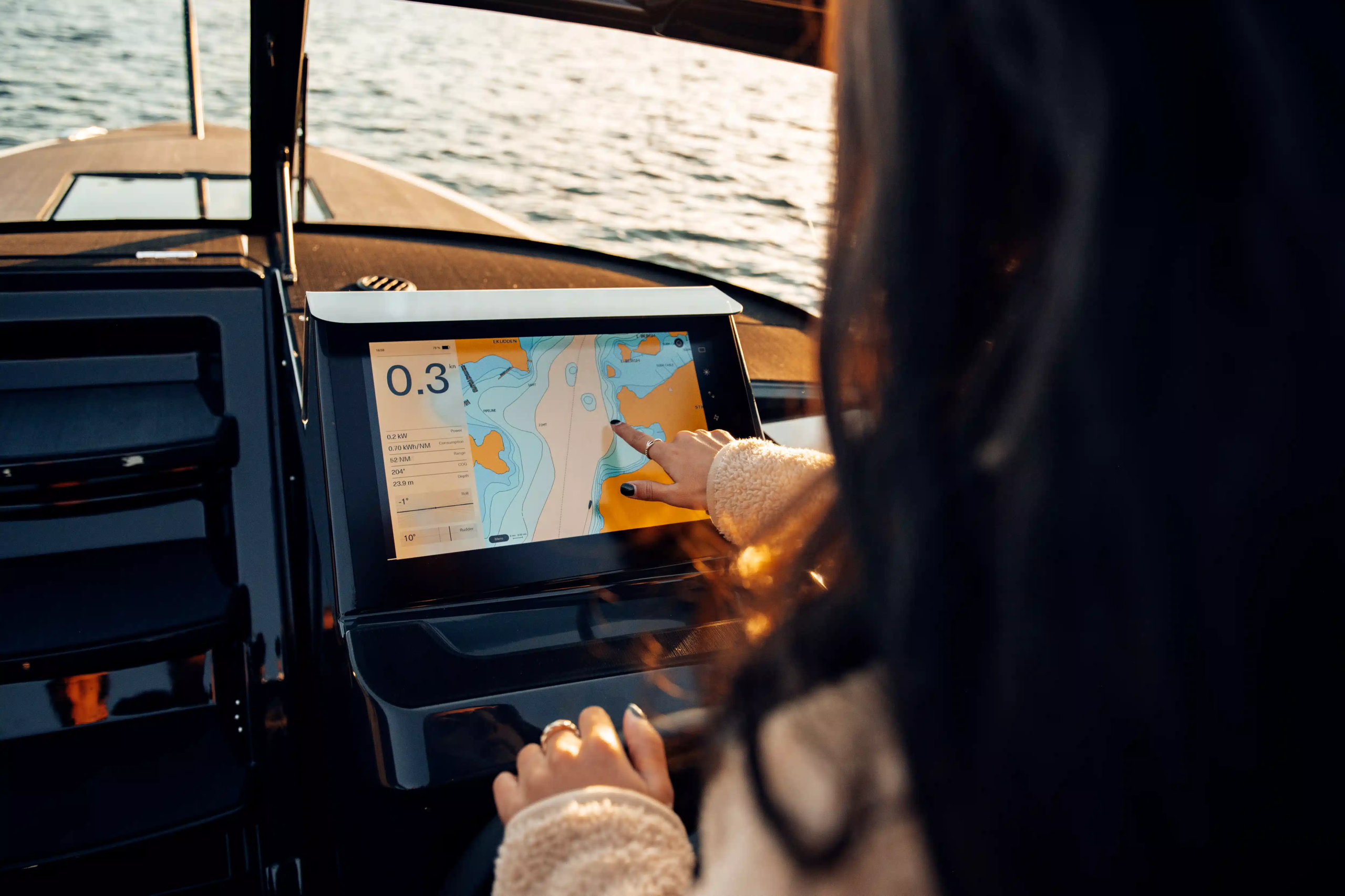
How do you charge electric boats?
You can charge electric boats using a household current or a standard Level 2 electric vehicle fast charger. It’s convenient and easy to do. Alternatively, you can find a three-phase outlet in marinas. Many marinas already have shore power installed, as most fossil fuel boats recharge their batteries there.
How long does it take to charge an electric boat?
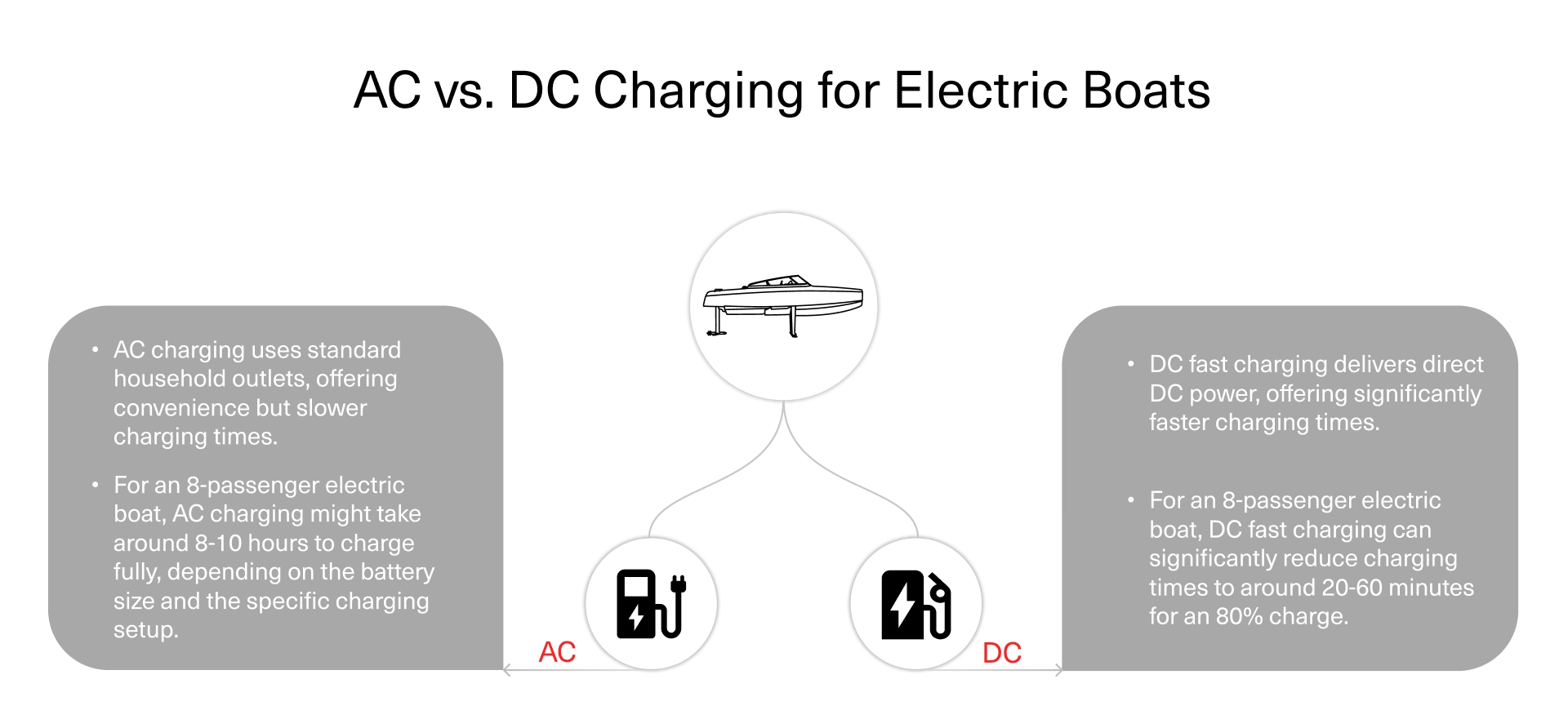
Charging a typical electric boat’s battery to 80 percent takes 8 to 10 hours on an AC charger, depending on the battery size. But it can be reduced to 20 to 60 minutes using a DC fast charger. So, the time needed for charging varies based on the type of charger used and the size of the battery.
How much does it cost to charge an electric boat?
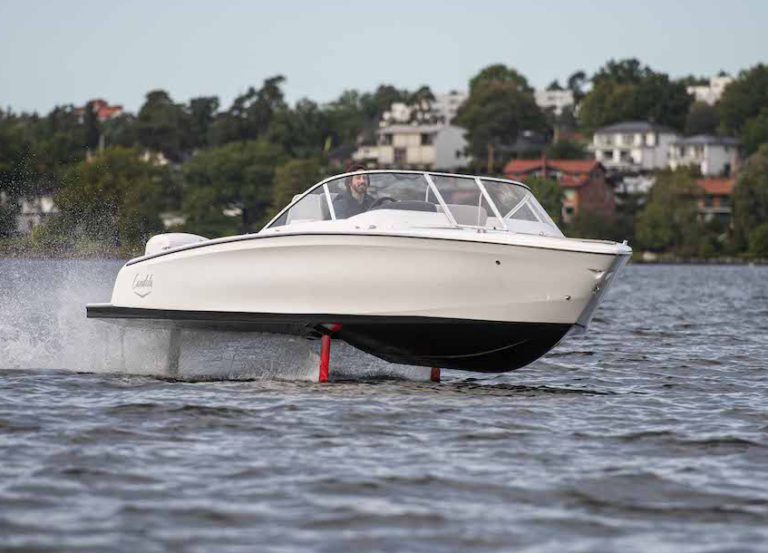
Charging an electric boat can cost just pennies a day, depending on local utility rates, but it’s notably cheaper than fuelling a combustion engine. A highly energy-efficient hydrofoil like the Candela C-8 uses approximately 70 kWh for over 50 nautical miles of range at high speed. In the Euro zone, a full charge amounts to around 10 euros.
How much power does an electric boat need?
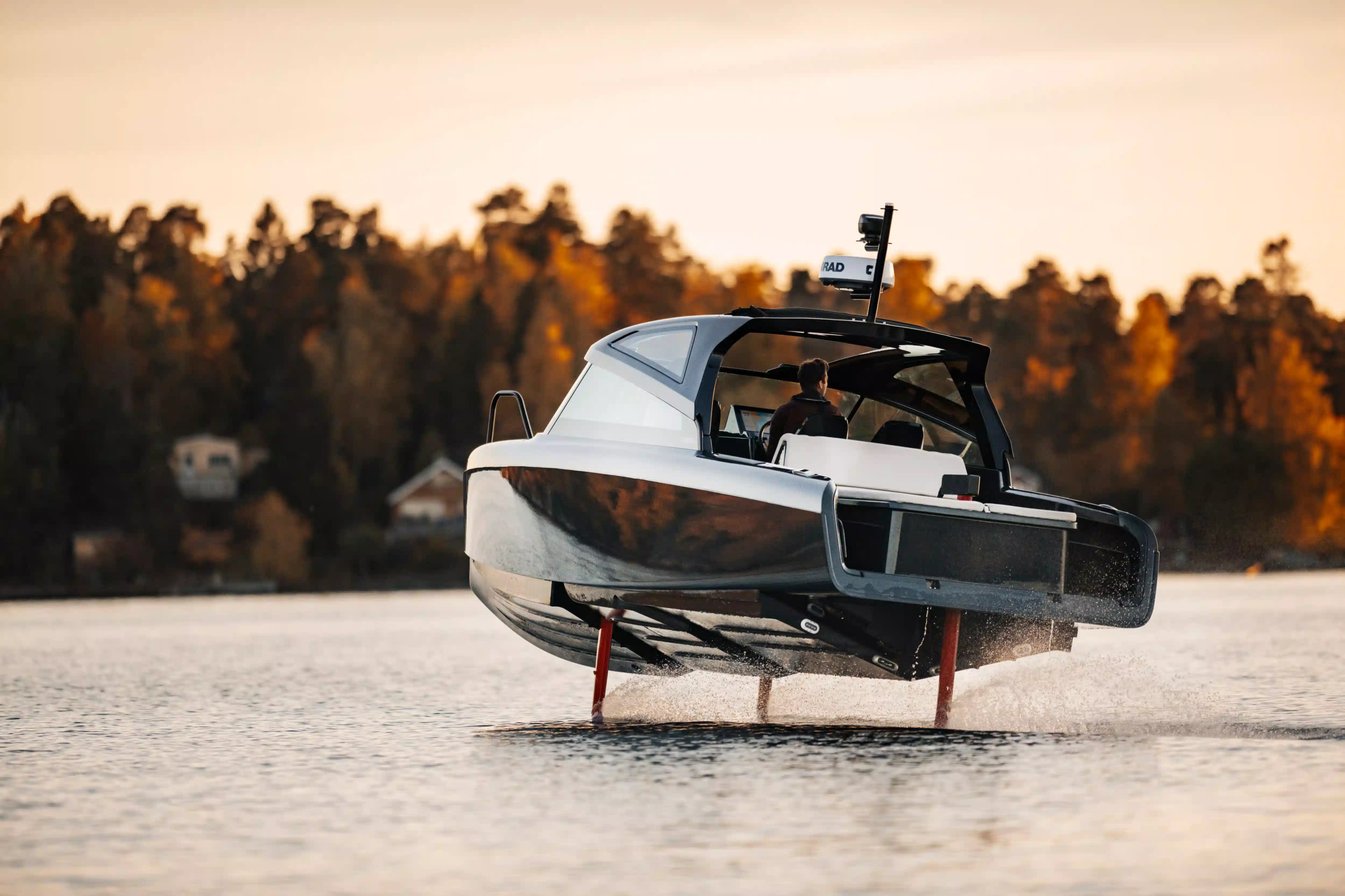
An electric boat typically requires about 2 kW of power per ton of boat weight for displacement boats, and 3 kW if navigating coastal waters or strong currents. For auxiliary purposes, a smaller motor can be enough. However, at high speeds, conventional electric planing boats need considerably more power, shortening the range to around 20-30 nautical miles. In contrast, hydrofoils can achieve over 50 nautical miles at speeds exceeding 20 knots, thanks to their smaller batteries.
What are the benefits of electric boating over traditional boating?
Electric boating offers several benefits over traditional boating, such as zero emissions, quiet operation, and lower operating costs, and preventing climate change, making it a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective choice. So, it’s a win-win situation for both nature and your wallet!
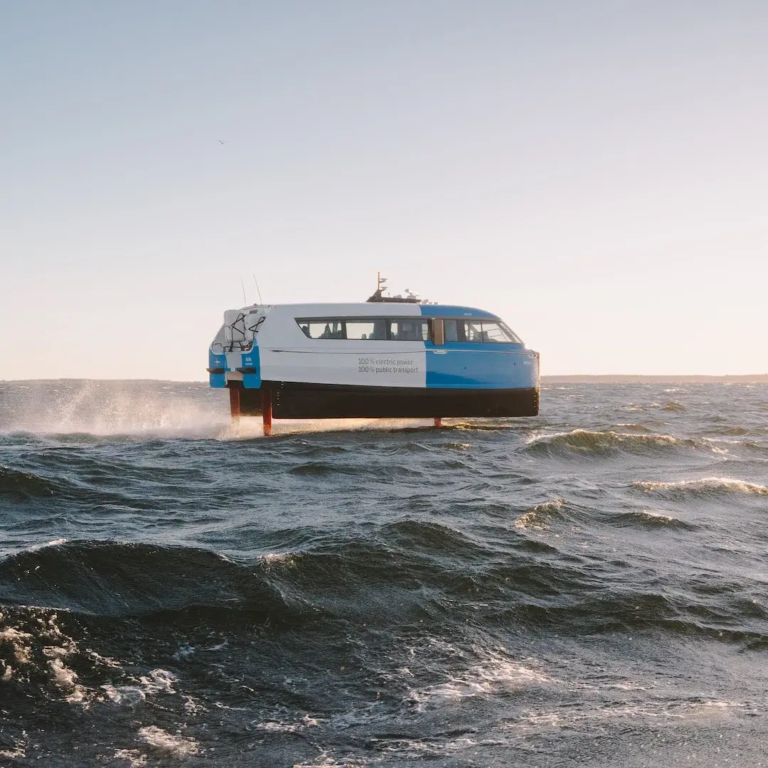
 Overview
Overview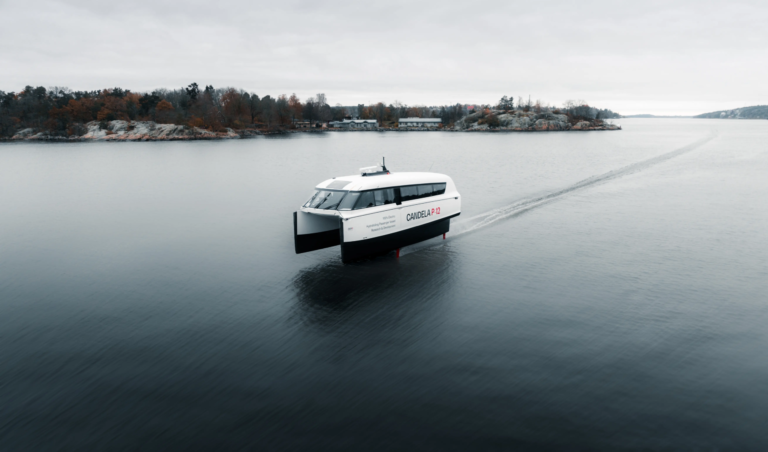  P-12
P-12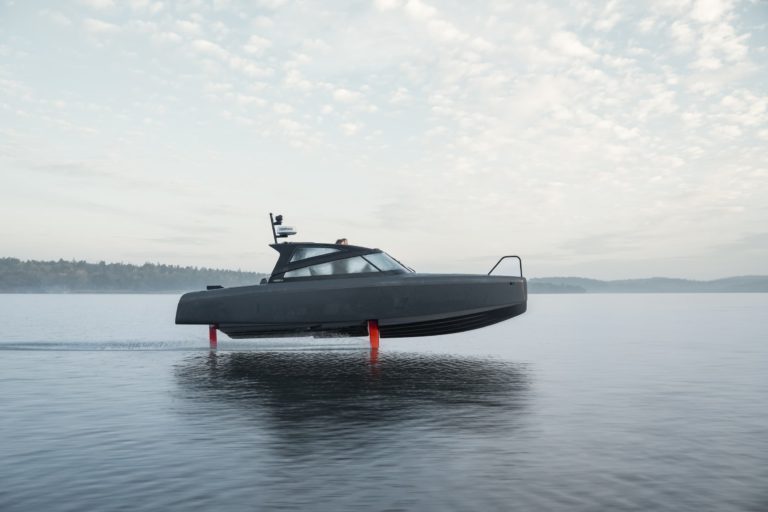 
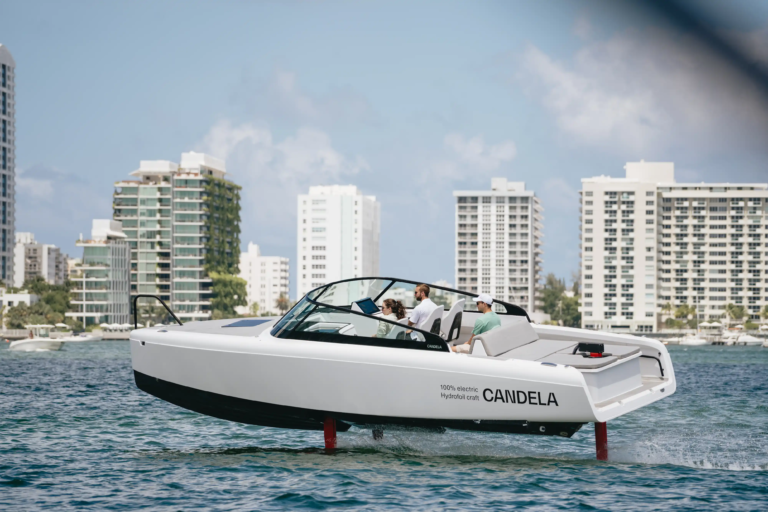 C-8
C-8