Introduction
Electric boats have a rich history dating back to the 19th century when the River Thames boasted a fleet of rental electric boats, supported by a network of charging stations in the 1880s.
However, the rise of petrol and diesel vessels, capable of higher speeds and longer ranges, led to a decline in electric boat usage.
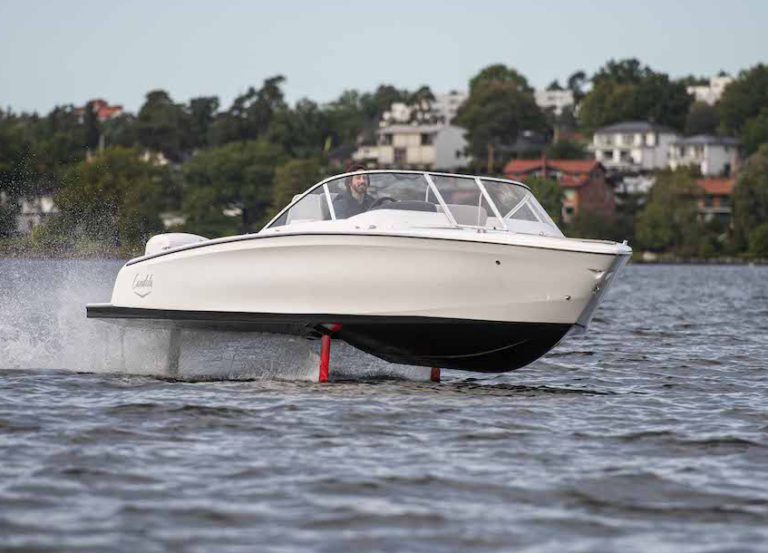
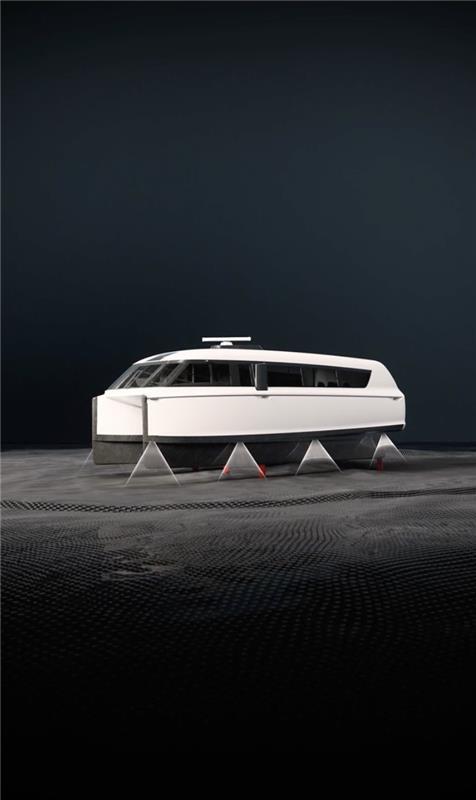
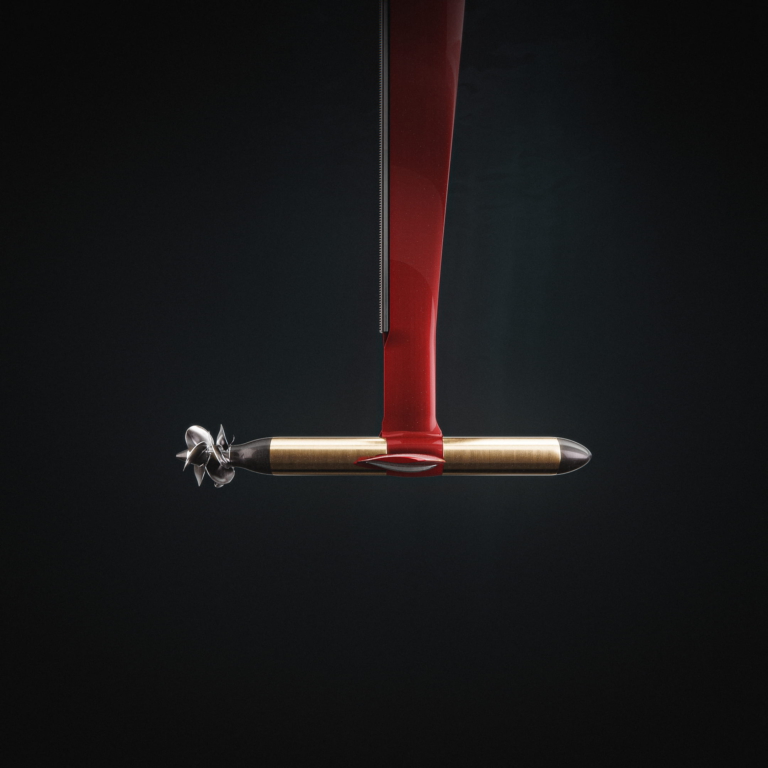
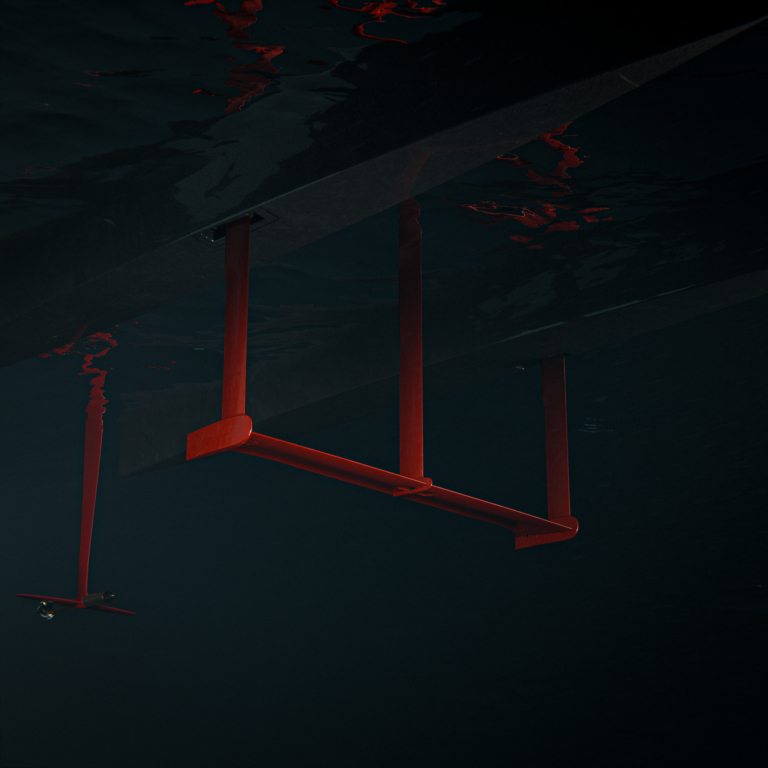
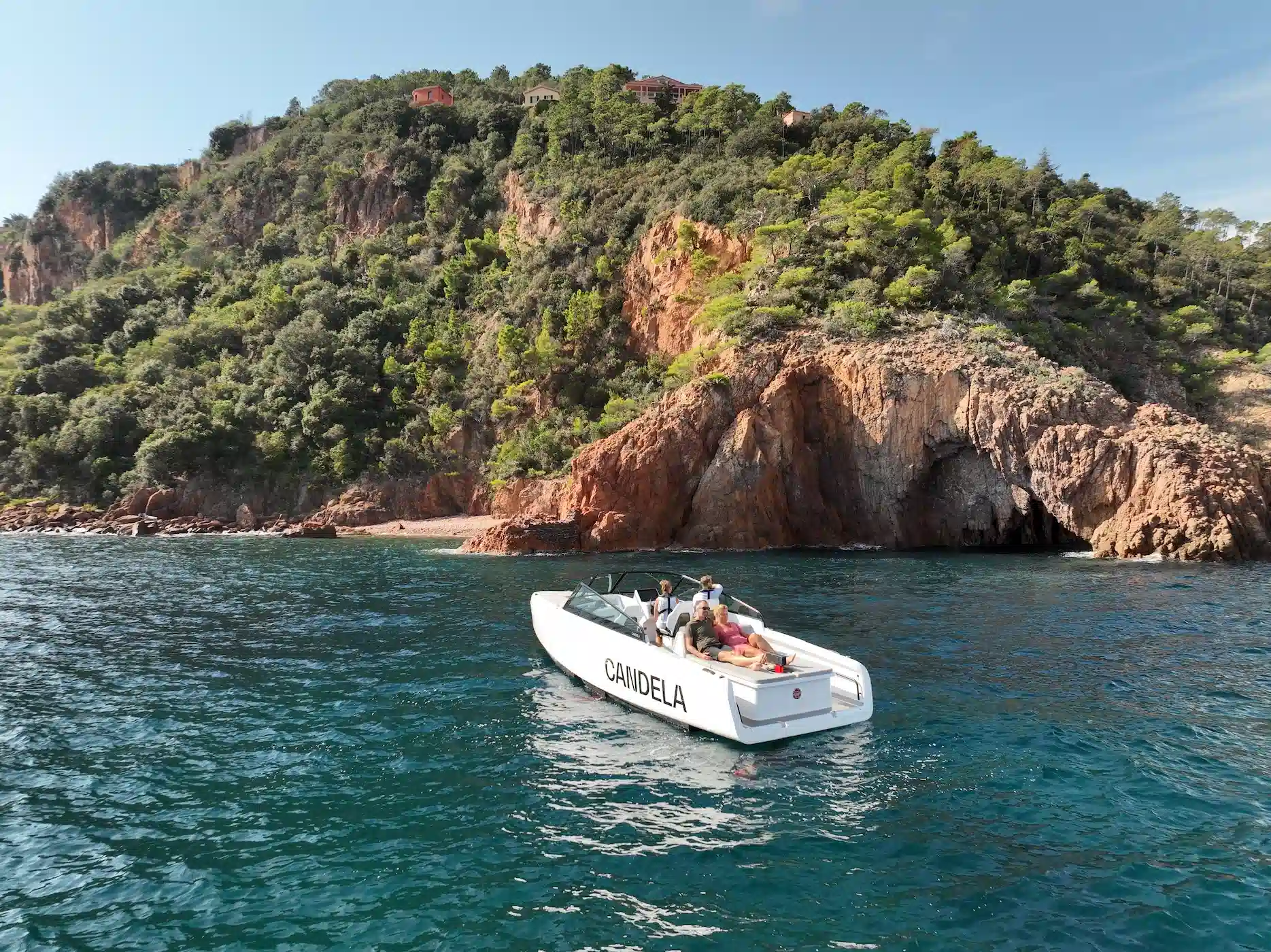
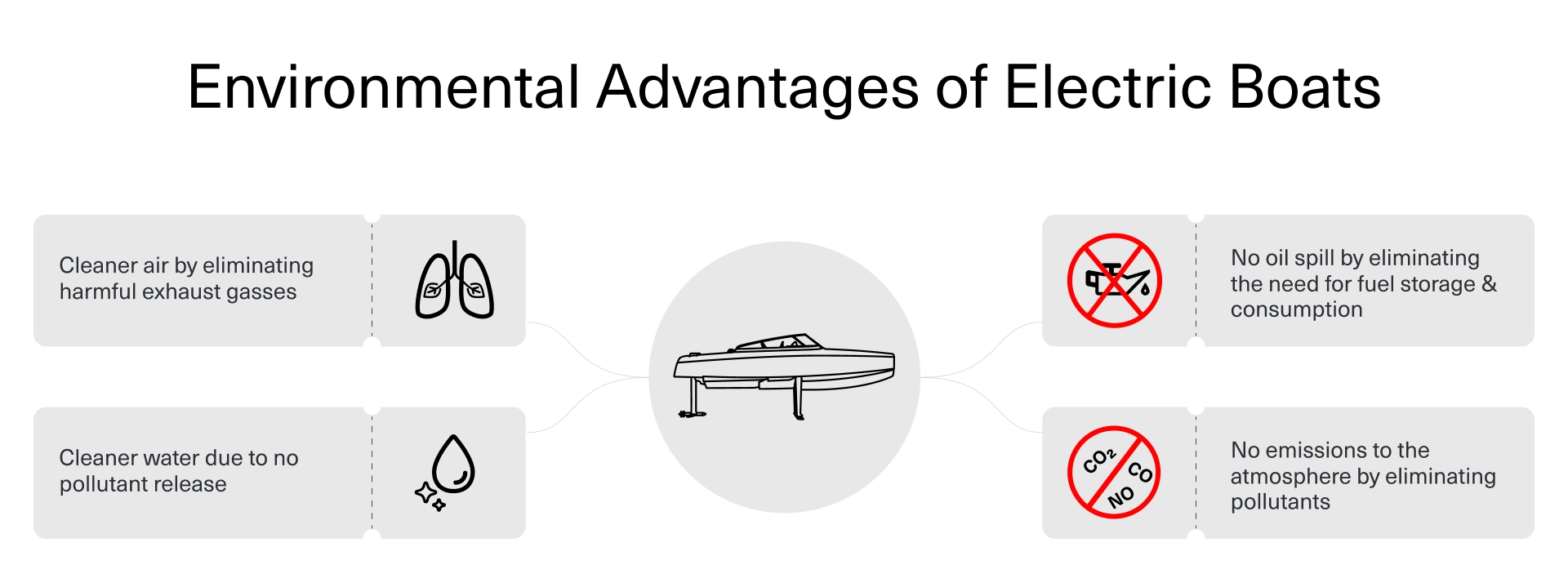
Despite this, electric crafts have carved a niche, particularly in environmentally sensitive areas where gasoline boats are prohibited by law. They offer quieter operation, are more cost-effective, and emit zero pollutants, contrasting sharply with traditional combustion engine boats.
To answer your question, no, electric boats are not all the same. But what exactly defines the current state of these boats in the modern world? Let’s explore further.
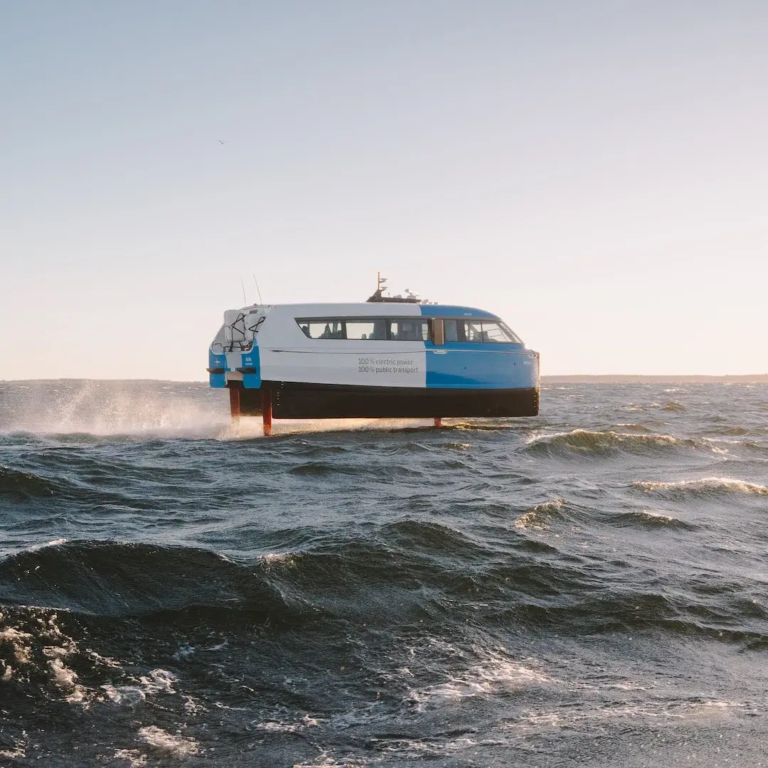
 Overview
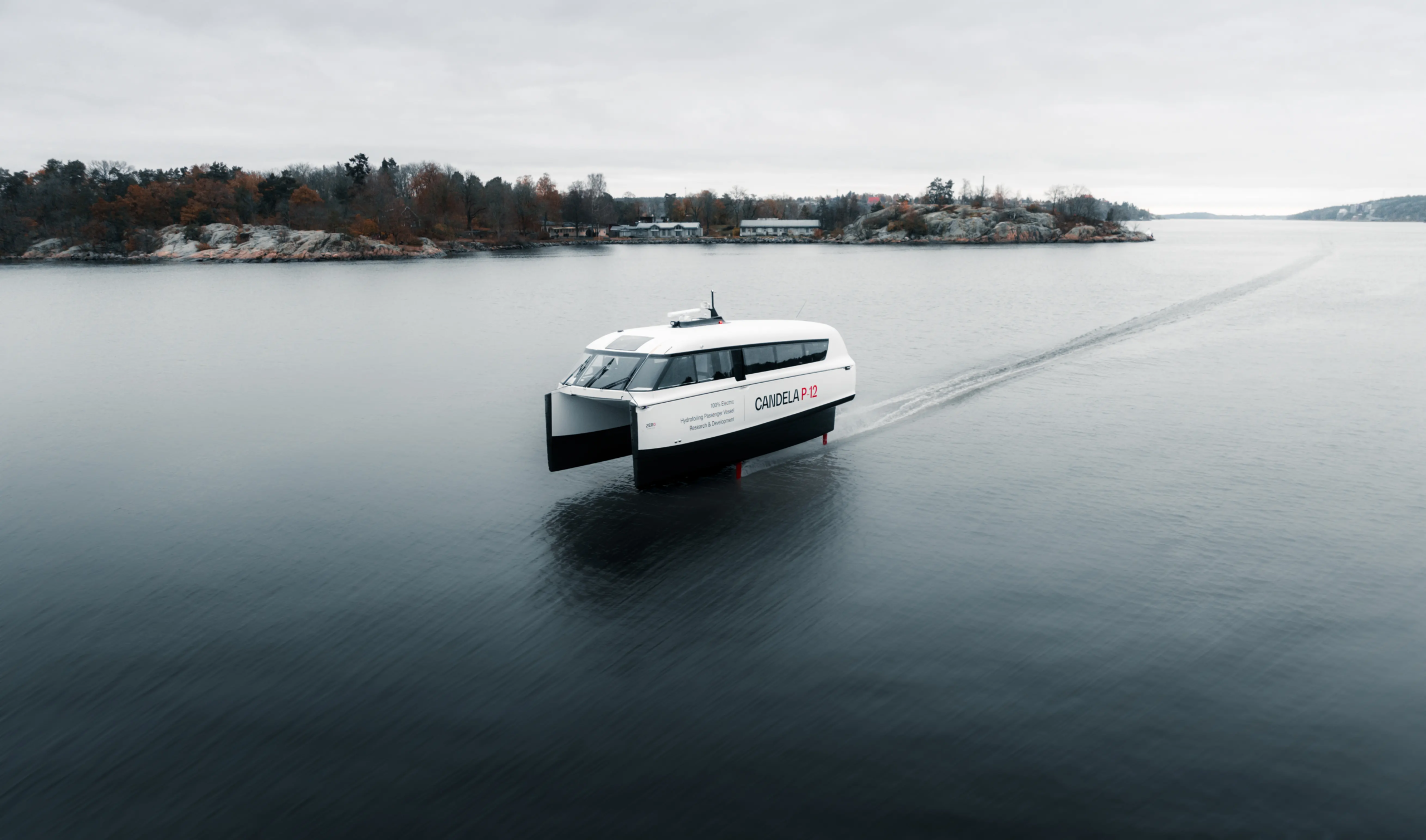
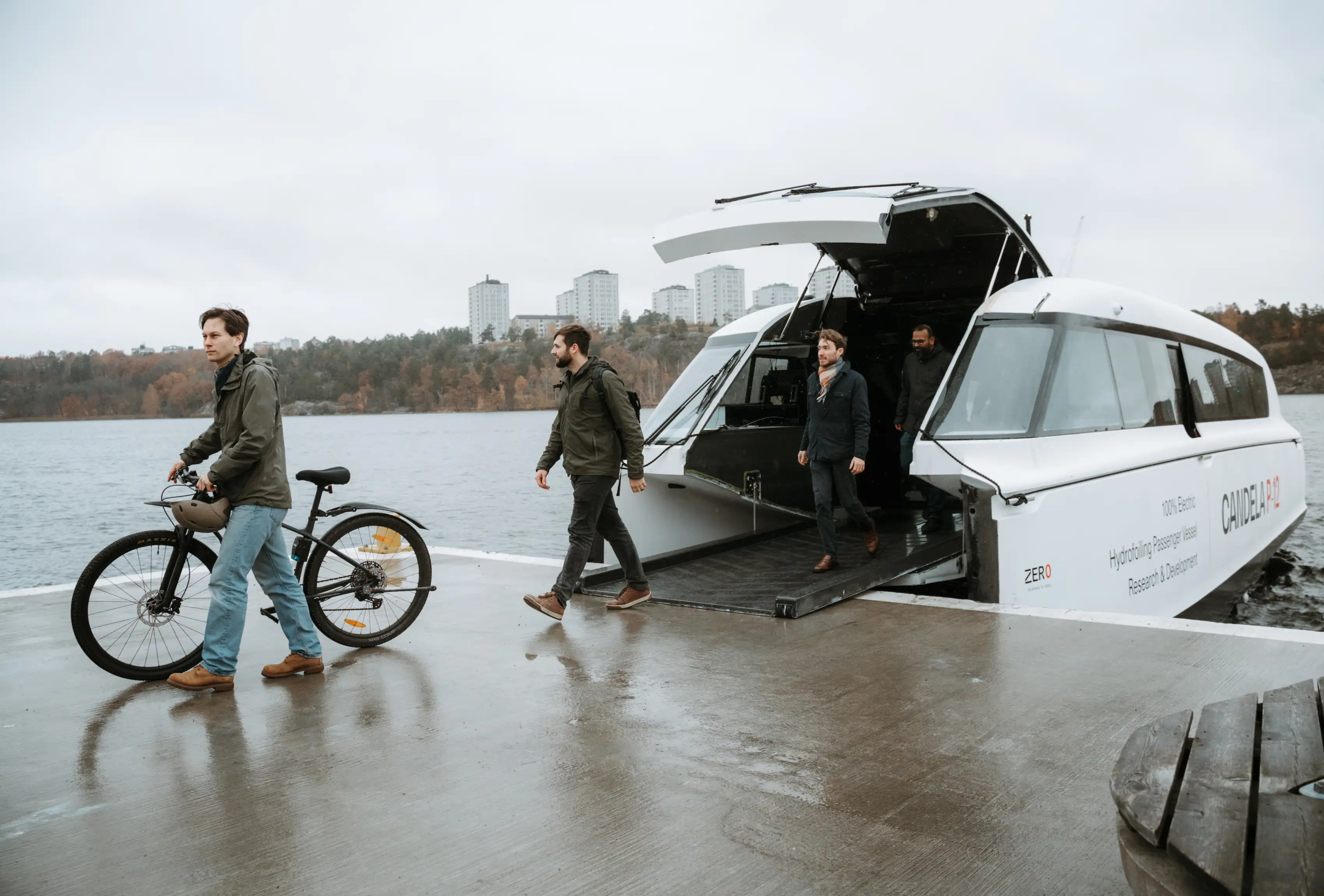
Overview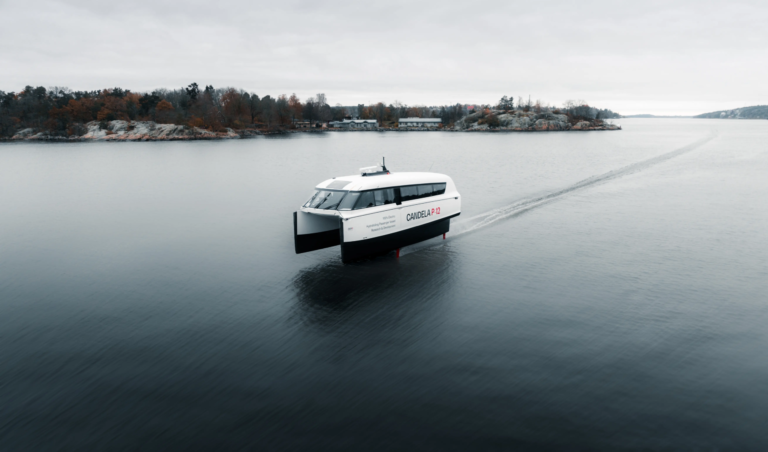  P-12
P-12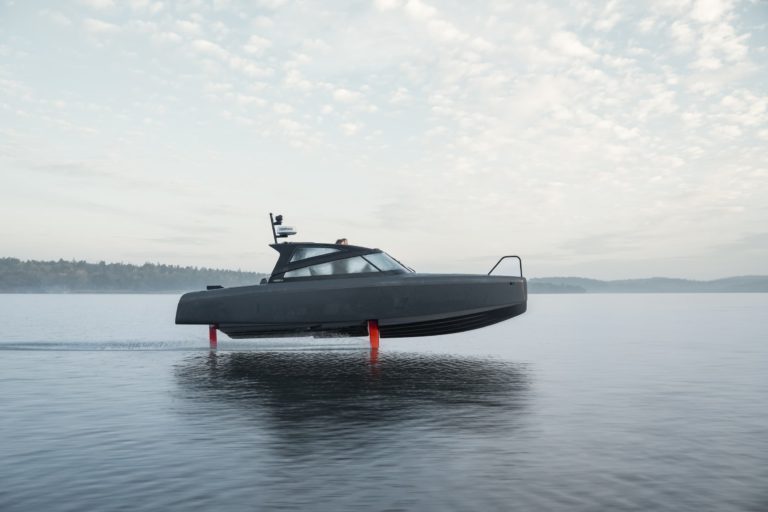 
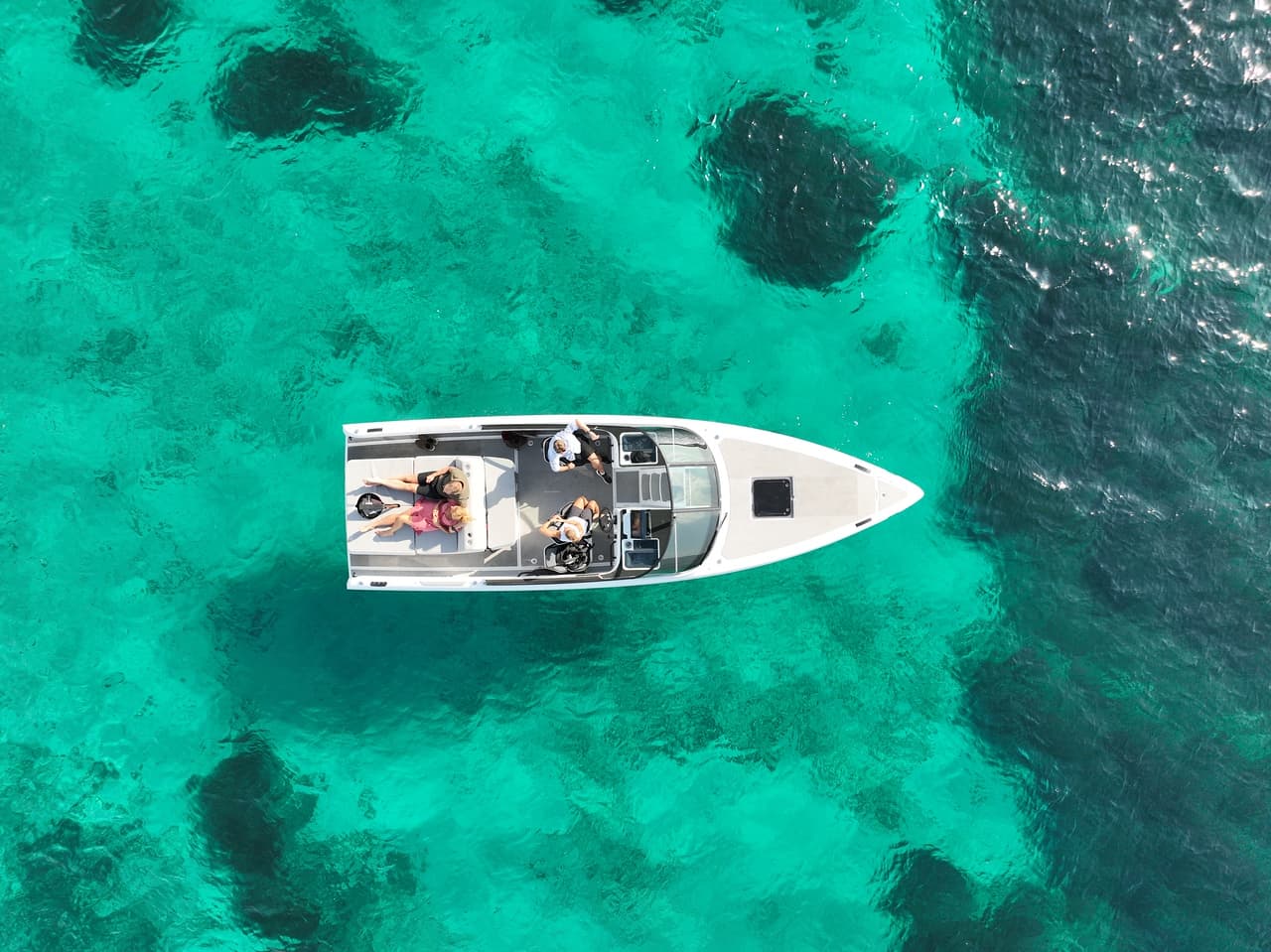
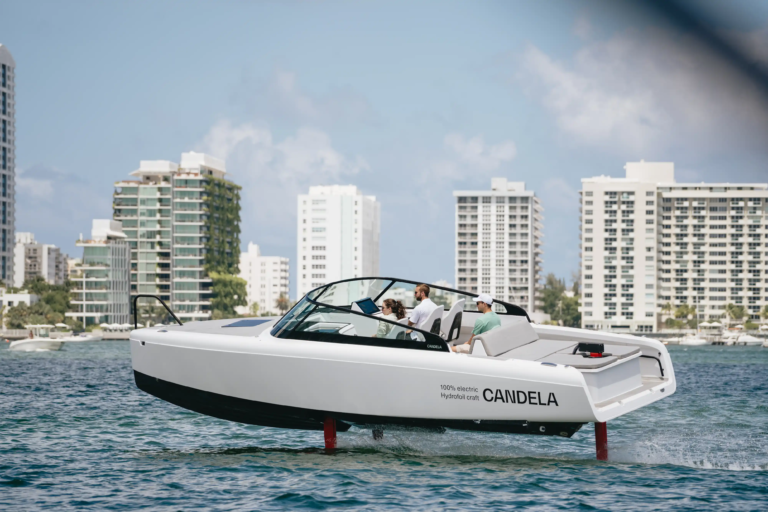 C-8
C-8